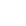
Chronic Venous Disease & Chronic Venous Insufficiency
The most common cause of chronic venous disease is reflux. Reflux is abnormal blood flow direction resulting from venous valve dysfunction. In the lower extremities’ thigh and calf, abnormal flow is from proximal to distal in deep or superficial veins, or deep to superficial in perforating veins. Reflux is most often primary (unknown aetiology and not present at birth), is less often secondary (known cause like trauma and thrombosis), and rarely congenital. Patient with reflux disease can easily overlook or forget symptoms of venous disorders due to their gradual onset or intermittent nature. Most of these patients do not have any visible varicose veins. Symptoms can worsen over time if left untreated.

The Venous System:
Superficial veins, veins located close to the surface of the skin. Deep veins-larger veins located deep in the leg.
Perforator veins-veins that connect the superficial veins to the deep veins. If you have varicose veins, the blood flow is low, your incidence to develop deep vein thrombosis is 9-fold higher than the normal population.
The Varicose Veins:
Veins have valves which allow blood to flow against gravity towards the heart. When these valves weaken and don’t function properly, they cause reflux and pooling of the blood into the leg veins because of gravity (especially on standing or sitting). These enlarged, swollen veins are known as varicose veins. If you have varicose veins, the blood flow is low, your incidence to develop deep vein thrombosis is 9-fold higher than the normal population.


Prevention
Symptoms:
-
Aching, fatigue, areas of redness on legs.
-
Tiredness, heaviness in legs, swelling (especially after standing/walking and in the evening.
-
Pain: Throbbing, burning of feet
-
Cramping (nocturnal, post exercise)
-
Sensation of swelling, swollen legs.
-
Burning of feet
-
Itching
-
Restless legs.
-
Varicose veins and spider veins (can be much more than just a cosmetic issue). Could be a symptom of a more serious problem.
-
Ulcers of the leg
-
Skin changes lower legs area (Brownish discolouration)
-
Bleeding
-
Hair loss, dryness lower legs
Most of the symptoms are generally worse later in the day, and are frequently relieved by leg elevation, activity and/or graduated compression hose. Varicose vein disease is a progressive disease, overtime, with worsening symptoms and possible complications such as thrombophlebitis, deep vein thrombosis, severe discomfort and leg ulcers.
Risk Factors to develop varicose veins/disease:
-
Female gender
-
Advanced age
-
Family history of varicose disease
-
Obesity
-
Deep Vein Thrombosis
-
Post-phlebitic syndrome
-
Occupations that require prolonged standing and walking
-
Multi-parity
-
History of leg injury
-
Frequent exercise was found to be protective for the development of venous disease.
-
Sedentary lifestyle.
-
Increased height and chronic straining when passing stools
Causes :
-
These symptoms are commonly associated with relatively static activity (think hairdressers, teachers or computer operators), and menstrual period or pregnancy (causes increase in hormone levels and blood volume, which in turn causes veins to enlarge.
Many factors contribute to the presence of venous reflux disease, including:
-
Family history of vein disorders (Hereditary is an important contributing factor)
-
Previous blood clots
-
Multiple pregnancies
-
Standing profession and sedentary lifestyle
-
Obesity
-
Heavy lifting
-
Constipation
-
Advanced age. (Due to loss of vein elasticity)
Since most veins lie deep to the skin surface, vein disorders are not always visible to the naked eye.
Who must be referred to a Specialist Vein Surgeon?
-
Patients with symptoms or recurrent varicose veins
-
Patients with skin changes, such as pigmentation (Brownish discolouration) or eczema, thought to be caused by chronic venous insufficiency
-
Thrombophlebitis and suspected venous incompetence
-
A Venous leg ulcer
-
A healed venous leg ulcer
-
Immediate referral to a specialist vein surgeon is warranted if there is bleeding varicose vein (Never use sutures)
How do to Diagnosis the cause of your vein problems ?
To determine if a venous problem exists, a comprehensive evaluation is performed through an in-depth medical history and a physical examination by an experienced specialist. In addition, an extensive duplex doppler done by an vascular sonographer to help determine a diagnosis. At Vein Solutions, the physician and patient mutually discuss the findings to determine the best treatment plan for the problem.
We are experienced in all vein treatment modalities and are able to recommend the best for the individual. The procedures are performed daily, in a patient-friendly environment and usually in less than an hour. Almost all procedures are done under local anaesthesia, thereby reducing risk and increasing convenience for the patient. Most patients resume normal activities within 24 hours.
Treatment:
Treatment is aimed at stopping venous reflux mainly the great saphenous vein and sometimes the small saphenous vein also. This is achieved by closing the diseased veins to restore normal venous circulation. In the past, surgical procedures for venous disease required general anaesthesia, large incisions, and long recoveries. Today, all procedures are now performed with minimally invasive technique in an outpatient setting -incision-less with little pain, and a rapid recovery and return to work.
-
Endovascular laser ablation is first line
-
If Endovenous laser ablation is unsuitable, offer ultrasound-guided foam sclerotherapy.
-
If ultrasound-guided foam sclerotherapy is unsuitable, offer only then stripping and phlebectomy
-
Do not offer compression stockings to treat varicose veins unless interventional treatment is unsuitable. They may relieve the swelling and aching of your legs but do not prevent more varicose veins from forming.

To treat chronic venous reflux problems, we offer at Vein Solutions
-
Our extensive experience. We are to do the endovenous laser ablation procedure in South Africa.
-
A comprehensive evaluation and management for individuals with lower-extremity venous disease and leg swelling.
-
Our Specialist Vein Surgeon are at the forefront of technology when it comes to treatment of varicose veins problems, leg swelling and venous leg ulcers.
-
We at Vein Solutions has led the way in the performance of minimally invasive vein surgery, and we take pride in our results and high patient satisfaction.
-
The very latest minimally invasive technology.
-
Treatment in our surgical rooms, on an outpatient basis, 25 clinics in South Africa.
-
Negligible pain.
-
Faster healing.
-
Walk-in Walk -out.
-
Surgical Expertise, Convenience, Advanced care and for your comfort.
You can return to normal activities immediately after the procedure, including walking, driving etc.
Compression Socks Tips
-
Get measured first thing in the morning or whenever your legs are the least swollen.
-
When putting on socks, don't gather them like you would pantyhose. Instead, hold the top edge of the sock and slip your toes and foot into the sock. Use the green gloves or other rubber gloves to smooth them into place. Or use the heel pocket out method as described on the back of this page.
-
Below knee compression socks should end 3-4 finger spans away from the bend of the knee. If your socks are long, don't pull on them very hard. Instead, ease them up your leg and calf until they end in the right spot.
-
Don't fold the tops of the socks down. That folded portion doubles the compression in that area and makes your leg swell below the fold.
-
Keep the socks smooth on your leg - wrinkles and folds will increase the compression in that one area.
-
If you are measuring yourself at home and your measurements fall on the border between a short and long length, pick the shorter length so that the sock won't be too long.
-
Hand wash compression socks or put them in a lingerie bag and wash them on cold in the washing machine. Hang them to dry, do not put them in the dryer. Do not use fabric softener as this will ruin some socks.
-
Compression socks should be worn daily - put them on first thing in the morning before your legs swell and take them off in the evening before you go to bed. Individuals who have legs that swell as soon as they are upright frequently need to put their compression socks on before they get out of bed.
-
Compression socks lose their strength after about 4-5 months when worn daily. Old compression socks should be thrown away.
-
It is a good idea to date your compression socks so that you remember how old they are.
-
If your socks feel too tight on your toes and feet, pull the toe of the sock out to give your toes a bit more room.